Deep Reads: Andreas Vilhelmsson’s journey into the world of global public health
The fifth entry for our Deep Reads blog series is written by Andreas Vilhelmsson, a post-doctoral researcher at the Department of Global Political Studies at Malmö University, Sweden. His research focuses mostly on patient reporting of adverse drug reactions and pharmaceutical regulation with respect to health policy and public health, but he is also interested in broader global health issues like climate change and welfare systems. Currently, he is also writing for the PLOS Student Blog due to his passion for writing and reaching a broader audience.
Laurie Garrett (2000). Betrayal of Trust: the Collapse of Global Public Health. New York: Hyperion
It’s not every day you read something that completely alters your perspective. A couple of years ago, I stumbled upon the book Betrayal of Trust: the Collapse of Global Public Health by Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist Laurie Garrett. At the time, as a PhD-student, I did not think of public health and genetics in the same sentence, but this changed upon reading this book. What Garrett did was to explore the conditions contributing to the epidemics she described and to stress the importance of genetics in current and future public health.
All of a sudden, public health was also a tale of global security and biological warfare; without the knowledge of modern genetics it would be impossible to comprehend such things as viruses, antibiotic resistance, immunology and inherited disease. You see, Garrett had not just written a book handling the present and future public health; Betrayal of Trust was also a guide to the history, in which Garrett describes, for instance, how Russian scientists had developed a genetically modified strain of anthrax that was resistant to all vaccines and antibiotics, and how nations voluntarily created genetically modified “superbugs”. The scientists she portrayed combined basic biology and public health in an unprecedented manner – it was almost like reading a thriller! Later, this kind of research led to the ethical discussions we have today regarding the controversial research on Avian Influenza A/H5N1, where scientists used mutant strains to construct a deadly virus.

Like no other author I had previously encountered, Garrett vividly described the resurgence and spread of drug-resistant strains of disease-causing microbes and the ongoing threat to our health they still represent. As a PhD student in public health, taking my first steps towards an unforeseeable future, this book captured me with the way it described the extraordinary capacity microbes have for generating genetic variation and thus developing antibiotic resistance. Of course I had some understanding of antibiotic resistance, but this was before the public health community and the world at large had begun to understand (at least in a noticeable way) and acknowledge the challenge antimicrobial resistance poses to global public health. Back then, it was more seen as a healthcare-related problem and not a public health problem. Now we know that the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria can even affect us outside the walls of the hospital.
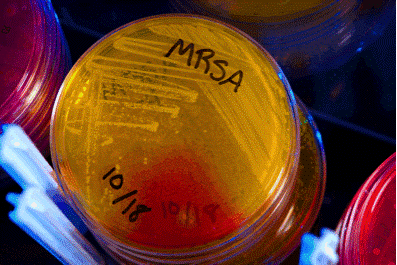
The Betrayal of Trust, in a very straightforward manner, gives its reader valuable insights in to how resilient and mutated strains of multidrug-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis-causing mycobacteria have evolved by natural selection and flourished, in part by the overuse and misuse of antimicrobial drugs. Once a triumph for global public health, tuberculosis has yet again become a problem, with drug-resistant strains of the microbe. Over time, Garrett writes, an intricate web of human activities had been directly promoting the evolution of bacteria and their resultant resistance to antibiotic drugs. Antibiotics were, and are, highly overused worldwide, and in nearly half of all common infections, inappropriately prescribed to treat viral rather than bacterial conditions. Widespread use of antibiotics in the livestock industry provides further pressure for the evolution of superbugs.

What is most saddening is the decline in public health on the global arena – almost to a state of chaos – that Garrett describes. In detail she explains how poorly prepared the world’s public health systems are to deal with disease outbreaks. Even with the expertise of modern medicine, people in the industrialized world may be surprised to find that they are totally unprepared for the challenges of a forthcoming global public health catastrophe.
As Garrett argues, we need to develop new and continuing global partnerships with an ambitious, comprehensive agenda to readdress public health policies for the intervention and prevention of epidemic infectious disease. Today, many of us trust the effectiveness of medical science and our public health systems for protection, but at the same time we live in a world in which new pathogens emerge and old infectious diseases can reemerge, mutated and even more dangerous than before. Here we have the genetic knowledge to work towards solving many of these threats, and I hope we start focusing on this as a wider community.
The Betrayal of Trust truly inspired me as a public health researcher and encouraged me to broaden my view on public health and understand all public health problems as essentially global public health problems. The book is a must-read for every public health student (and everyone else!).

The bacteria have a mind-boggling repertoire of genetic mechanisms leading to genotypic and phenotypic change – you name it and they have it – point mutations, deletions, inversions, insertions, gene conversion, site-specific recombination, homologous recombination, phase variation, slipped strand mispairing, insertion sequences, transposons and integrons. These have enabled bacteria to survive on this planet for more time than any other living being – approximately 4 billion years, braving six episodes of major extinctions of life on this earth. The dismal scenario of antibiotics or antimicrobial resistance (AMR) all over the globe is alarming, which has been highlighted on numerous fora and by a recent insightful publication from the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics and Policy (CDDEP) titled – The State of the world’s antibiotics, 2015. I completely agree with the author of this post that we have to start focusing on these issues of public health concern as a wider community with the hope that innovations in science and technology will give us an equal edge to confront the versatility of microbes in this arms race between the man and the microbes.
Jugsharan Virdi, University of Delhi South Campus, New Delhi 110 021, India
[…] You will find a longer description of how this book affected me in a post I wrote for PLOS Biologue in 2015 […]
[…] You will find a longer description of how this book affected me in a post I wrote for PLOS Biologue in 2015 […]
[…] I have written elsewhere, inspiring people have the ability to change the course and intensity of your research area, in my […]